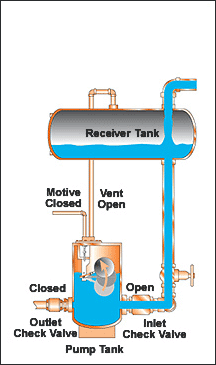
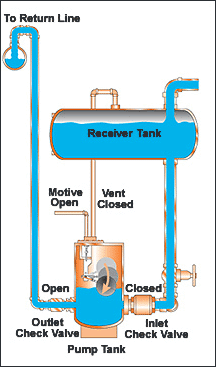
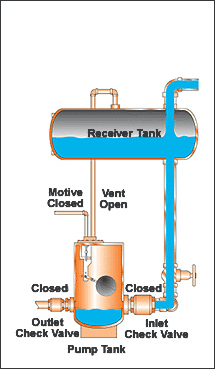
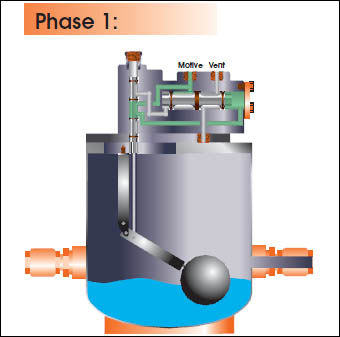
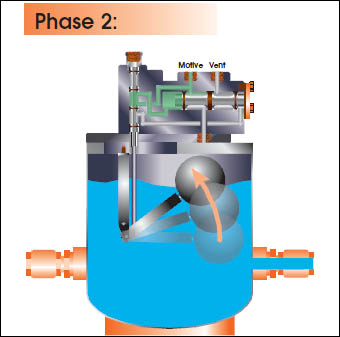
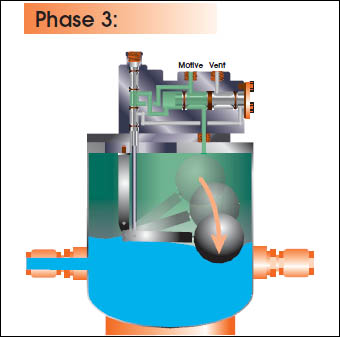
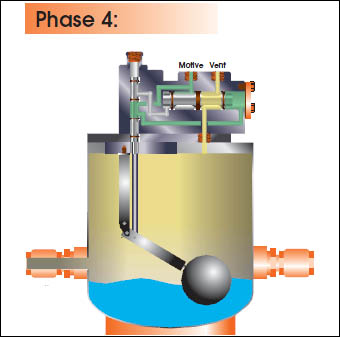
CEMLINE® non-electric condensate pumps have many advantages. There are no impellers or seals, or cavitation problems and no electricity is required. Condensate is efficiently moved at reduced operating cost.
CEMLINE Condensate Pumps (CCP Series) use compressed air or steam as a motive force to move condensate. Condensate from steam systems needs to move from points of lower elevation to points of higher elevation, from points of lower to higher pressure, or from a vacuum to a point of higher pressure or elevation.
Traditionally, condensate is transferred with the use of electrically operated condensate pumps. When moving condensate with electric pumps, the electric pumps tend to wear out quickly. Electric condensate pumps have impellers and seals which can wear, leak, or break down due to harsh condensate environments. The benefit of using non-electric condensate pumps instead of electric condensate pumps is the non-electric condensate pumps have no impellers or seals to wear, requiring less downtime and maintenance. In addition, some remote locations exist where electrical service is not readily available or it is hazardous to use electricity.
Additional benefits from the use of non-electric condensate pumps is the reduction of operating costs associated with returning hot condensate to the boiler. Typically, electric condensate pumps require the condensate flash to atmospheric pressure and decrease in temperature before being pumped to the boiler. The non-electric condensate pumps reduce costs compared to electric condensate pumps because the non-electric condensate pumps can return condensate to the boiler at a higher temperature, which reduces the heating costs required to re-heat the condensate. Along with the reduced expense of re-heating of condensate, less water treatment chemicals are required and less make up water is required to be added to the system.